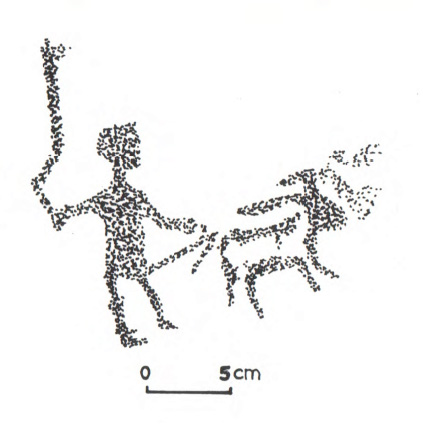
A paper by the AcrossBorders project on the application of strontium isotopes to investigate cultural entanglement in Sai and its surroundings was just published (Retzmann et al. 2019)! In this study, strontium isotopes were applied to identify possible ‘colonialists’ coming from Egypt within the skeletal remains retrieved from Tomb 26 of the pharaonic cemetery SAC5 on Sai Island.
The local strontium signal on Sai Island during the New Kingdom was derived from archaeological animal samples (rodent, sheep/goat, dog and local mollusc shells, all dating from the New Kingdom) in agreement with local environmental samples (paleo sediments and literature Sr isotope value of Nile River water during the New Kingdom era).
As outlined in the article, the strontium values suggest that all people buried in Tomb 26 are members of the local population. A striking outcome, since the tomb, the tomb equipment, the personal names and titles are all clearly ‘Egyptian’.
These fresh results tie in nicely with research at other main Upper Nubian centres like Tombos (Smith and Buzon 2017) and Amara West (Buzon and Simonetti 2013) – and will be of great importance also for DiverseNile. More information on the complex coexistence and biological and cultural entanglement of Egyptians and Nubians during the New Kingdom are urgently needed.

In this respect, we will continue to investigate the isoscape of Upper Nubia further, enlarging our scope with my new concession – I am very happy that the successful team around Anika who did this for Sai will be again involved! The MUAFS area will provide new data from soil, water, molluscs and of course animal bones and human teeth which will allow us to place the data from Sai in a broader context. The periphery of Sai and Amara West, our Attab to Ferka region, has rich potential to check the validity of our present strontium analysis.
References
Buzon and Simonetti 2013 = Buzon, M. R. and Simonetti, A., Strontium isotope (87Sr/86Sr) variability in the Nile Valley: identifying residential mobility during ancient Egyptian and Nubian sociopolitical changes in the New Kingdom and Napatan periods, American Journal of Physical Anthropology 151, 2013, 1-9.
Retzmann et al. 2019 = A. Retzmann, J. Budka, H. Sattmann, J. Irrgeher, T. Prohaska, The New Kingdom population on Sai Island: Application of Sr isotopes to investigate cultural entanglement in ancient Nubia, Ägypten und Levante 29, 2019, 355–380
Smith and Buzon 2017 = Smith, S. T., and Buzon, M. R., Colonial encounters at New Kingdom Tombos: Cultural entanglements and hybrid identity, 615–630, in: N. SPENCER, A. STEVENS and M. BINDER (eds.), Nubia in the New Kingdom. Lived experience, pharaonic control and indigenous traditions, British Museum Publications on Egypt and Sudan 3, Leuven 2017.