Summer term is approaching an end at LMU (finally!) and there is again some time for research. I am currently busy with processing the pottery from AtW 001, but I also managed to work on the Kerma cemetery GiE 003. Our two student assistants, Caroline and Iulia, have been very hard-working in digitalising the original pottery drawings.
A topic that concerns me at the moment is the question of lids or covers for pots. In Egypt, ceramic lids are well attested since the earliest time. During the New Kingdom, it is sometimes really tricky to decide whether a shallow small dish was used as a lid or as an actual dish. In addition, reused sherds are commonly utilized as covers for pottery vessels (see also evidence from Sai Island, Budka 2020, 250, fig. 117).
How much do we know about lids and covers of pottery vessels from Nubia? Not a lot I am afraid (ast least I don’t).
Brigitte Gratien included some special types of lids in her corpus of the pottery of the Classical Kerma period (Gratien 1978, 36, fig. 7; fig. 63, type 19 and type 32, decorated lid). These are all specific for the site of Kerma and haven’t been found elsewhere. Type 32 of Gratien is especially noteworthy. It is a series of painted vessels with covers, which were interpreted as imitation of basketry or even as representation of a hut (Bonnet 2004, 83). For me, the interpretation of an imitation of basketry is more convincing, also because such imitations in pottery already exist much earlier, though with incised decoration (for nice examples, including pots with lids, see Old Kingdom Elephantine, Raue 2014, fig. 182).

Interestingly, other than these basketry imitations from Elephantine, I do not know of any lids or covers of Nubian pottery prior to the Classical Kerma age. Could pots have been covered with non-ceramic materials – like with basketry or some other organic materials? And could the increase in pottery lids at the capital in Kerma during the heyday of the empire maybe reflect an inspiration from the Lower Nile/Egypt? Or something else? Another possibility is that we simply missed pottery lids in the Nubian ceramic tradition because we interpreted dishes and cups wrongly (as dishes/cups and not as lids).
These are all intriguing questions, and I will try to investigate them in more detail soon. For now, I would like to present some interesting case studies from the newly excavated Kerma cemetery GiE 003.
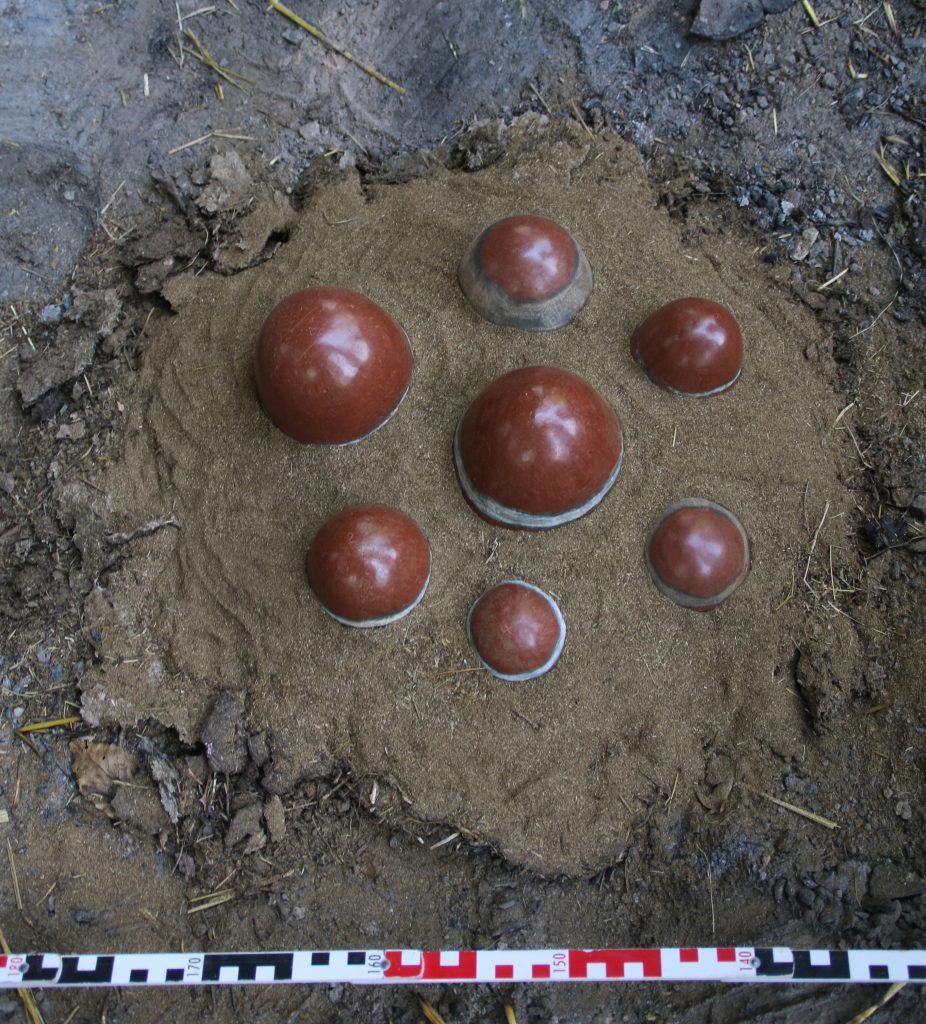
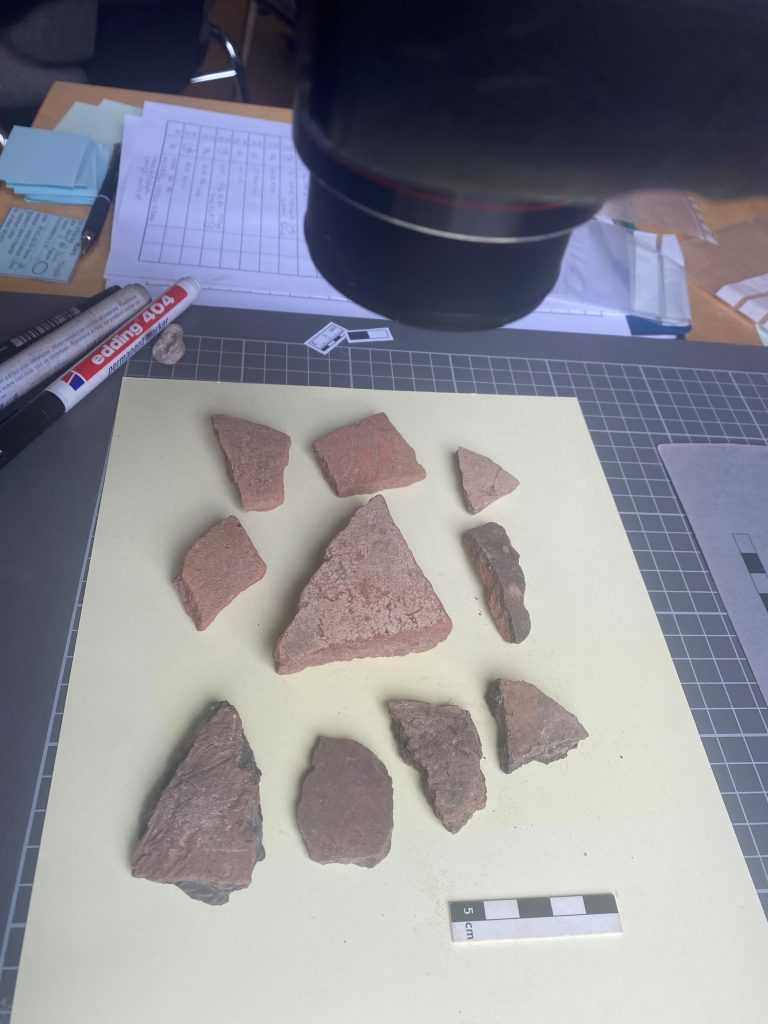
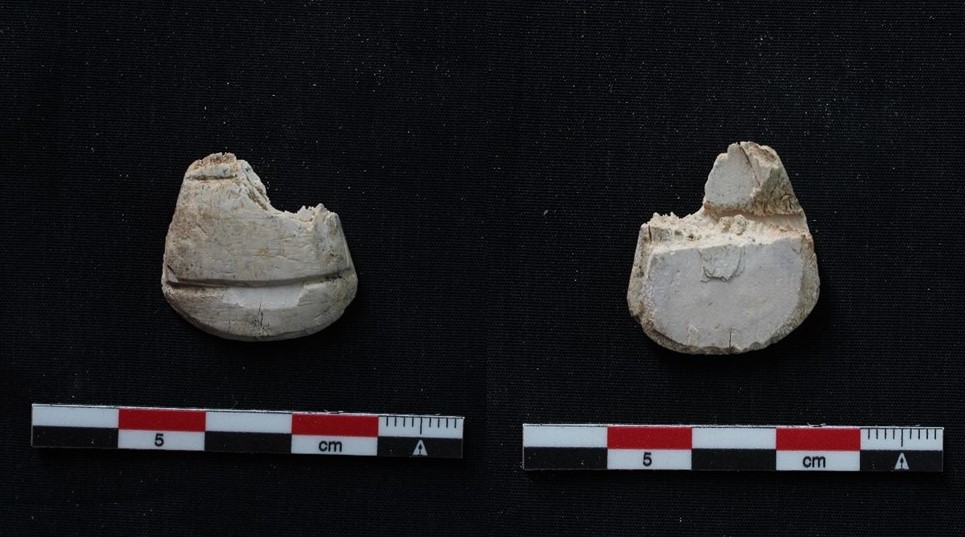
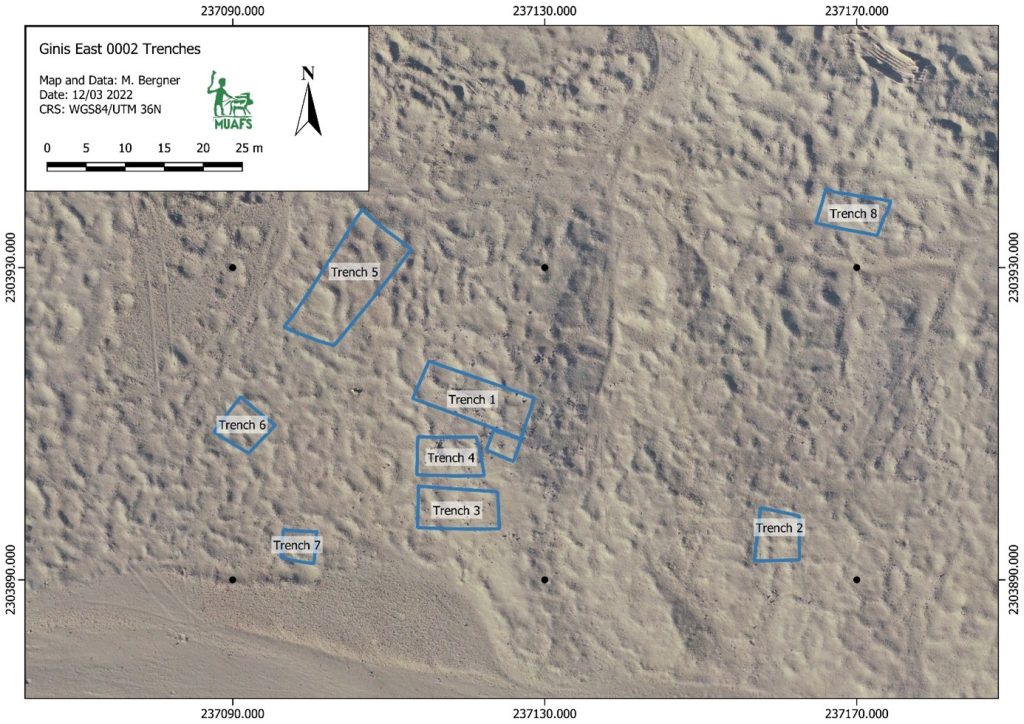
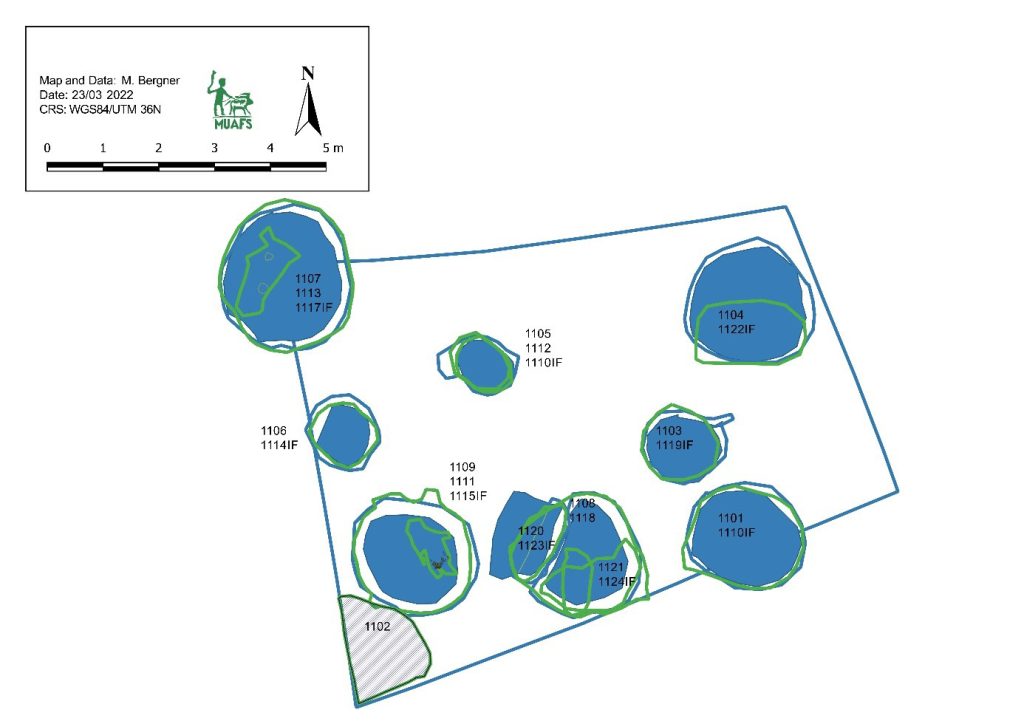
Feature 20 in Trench 1 is a rectangular burial pit with rounded edges, vertical walls, and impressions/pits in the east (40cm x 10cm) and west (30cm x 10cm). Remains of a contracted burial were still found in place on a wooden funerary bed. A goat/sheep offering and three almost complete pottery vessels were found below the foot end of the bed on the west side. The complete set of a red-burnished Kerma pot with a stone lid found in situ on top of the vessel (MUAFS 61 and 62) is especially remarkable.
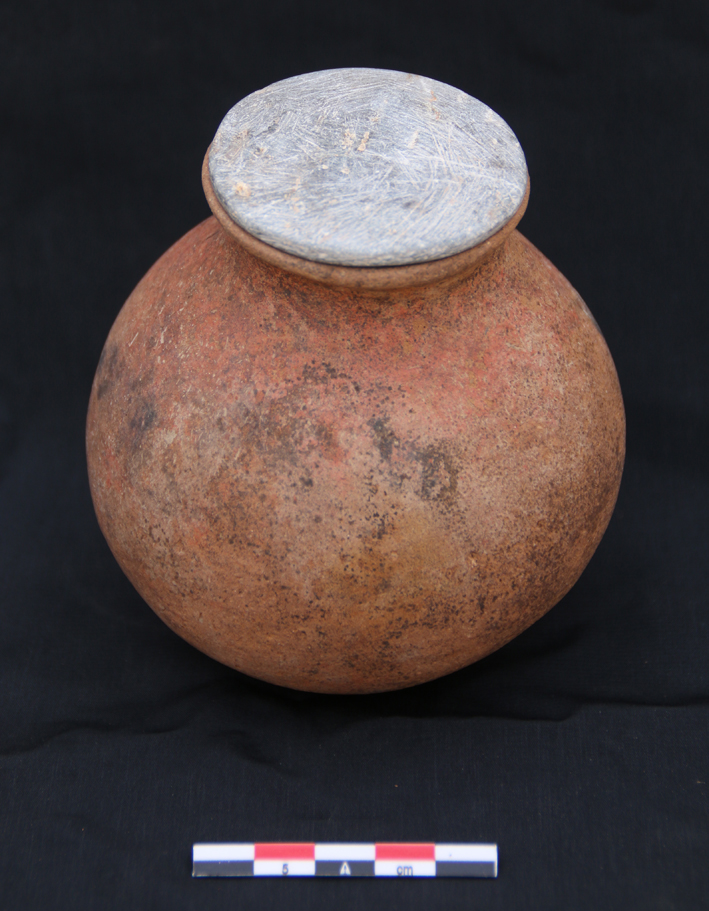

The lid is just a nicely shaped circular disc without any modelling of the interior as it is for example known from lids of kohl pots. With a diameter of 5.4cm it fits perfectly on the pot. Some of you will wonder: with an in situ lid on the pot – what did they find inside the vessel? Well, to my disappointment the pot was completely empty except for some dust.
However, the stone lid MUAFS 62 is not a singular piece from GiE 003. Another stone lid was found in a plundering layer, MUAFS 10. Although it was impossible to associate this piece with a proper burial or feature, it is more or less contemporaneous to MUAFS 62 and can be attributed to the Classical Kerma time. With a diameter of 6.2cm it is slightly larger than MUAFS 62.
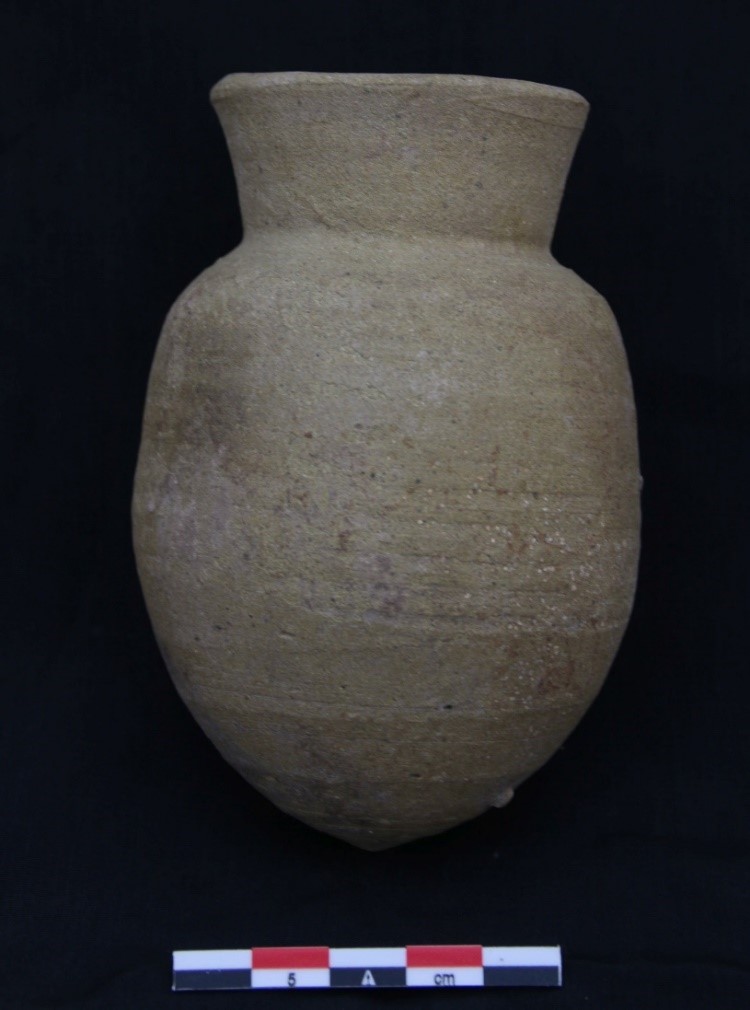
Apart from these two stone lids used as covers for pottery vessels, Trench 1 of GiE 003 also yielded a pottery lid. An almost complete lid, MUAFS 312-1/2022, was found in Feature 10 (a rectangular burial pit with pits for the funerary bed, very similar to Feature 20). This pottery lid is wheel-made, was imported from Egypt and is made in a Nile clay B2 variant. Such vessels are very common in the 17th Dynasty in Egypt (e.g. at Elephantine). With a diameter of 10.7cm and its convex shape, it is markedly different to the stone lids mentioned above.
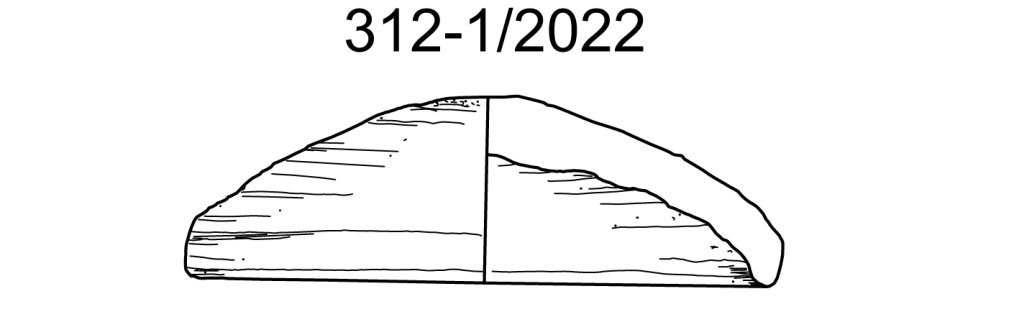
Although proof is lacking, I would assume that this pottery lid was used as the cover for one of the few Marl clay vessels imported from Egypt attested from Trench 1. However, the pottery found inside of Feature 10 apart from the lid was all Kerma in style, including typical Black topped fine wares.
To conclude, it requires more in situ found assemblages like MUAFS 61 and 62 to answer broader questions about the use of lids in Nubia in general and Kerma cemeteries in more particular. For now, the evidence from GiE 003 suggests some intriguing variation, especially in the Classical Kerma age.
References
Bonnet 2004 = C. Bonnet, Catalogue no. 57: Vase with cover, in: D.A. Welsby and J.R. Anderson (eds.), Sudan. Ancient Treasures. An Exhibition of recent discoveries from the Sudan National Museum, London 2004, 83.
Budka 2020 = J. Budka, AcrossBorders 2: Living in New Kingdom Sai. Archaeology of Egypt, Sudan and the Levant 1, Vienna 2020.
Gratien 1978 = B. Gratien, Les cultures Kerma. Essai de classification, Lille 1978.
Raue 2014 = D. Raue, Elephantine und Nubien im 4. – 2. Jahrtausend v. Chr., Habilitation thesis, Leipzig 2014 (published in 2018, Berlin).