I am delighted that Volume 45 of the journal Egitto e Vicino Oriente has been published, including my own contribution about Kerma cemetery GiE 003 in Attab/Ginis East (Budka 2022).
The aim of this paper was to present the preliminary excavation results of this large Kerma cemetery on the outskirts of Sai. Based on our excavation results from 2022, we know that it was continuously used from Middle Kerma to Classic Kerma times and has close parallels to cemeteries in Batn el-Haggar (especially at Ukma). Our excavations allow a better understanding of rural Kerman funerary practices and the types of imported objects that are present or missing within these communities (such as scarabs, pottery vessels), demonstrating local prosperity and the superregional interconnectedness of these groups.
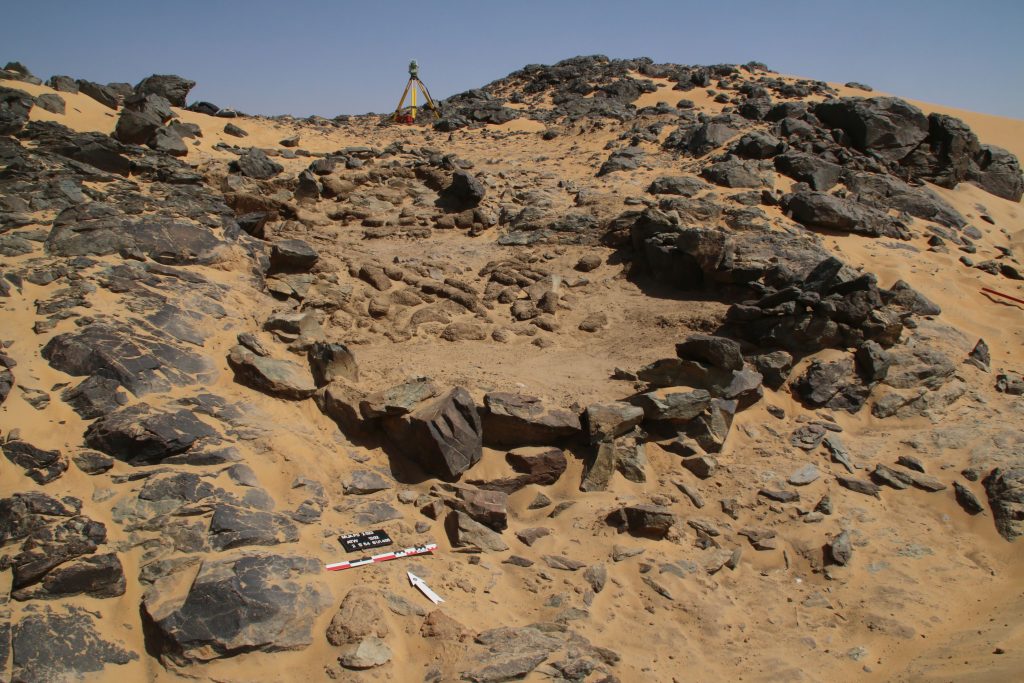
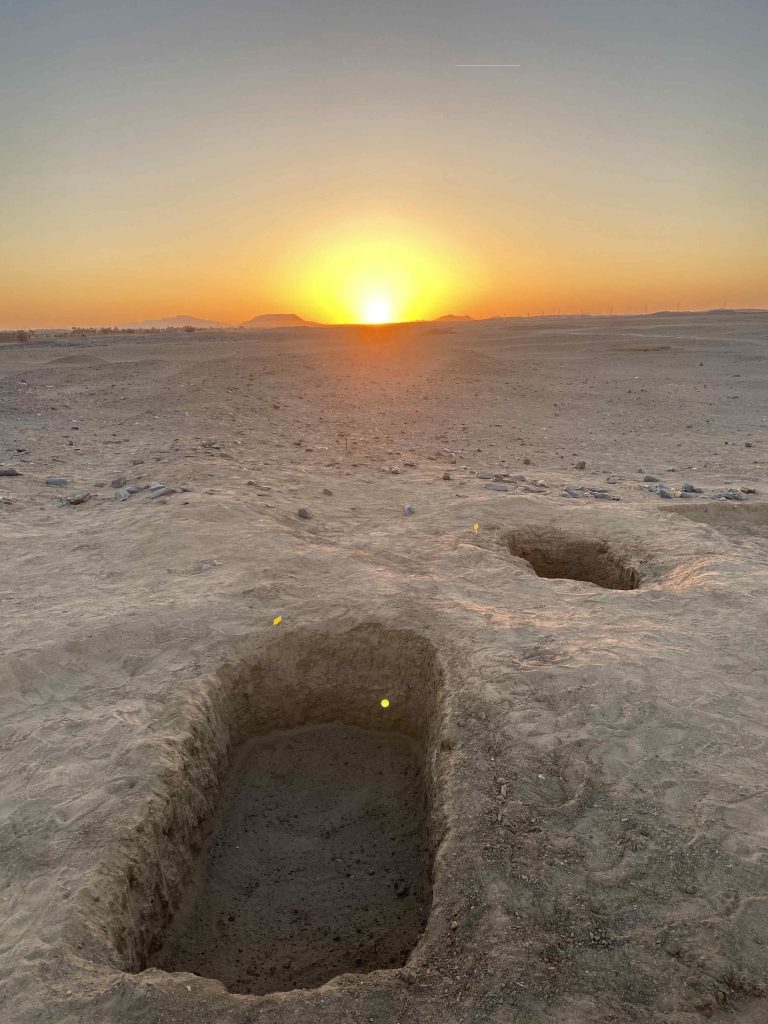
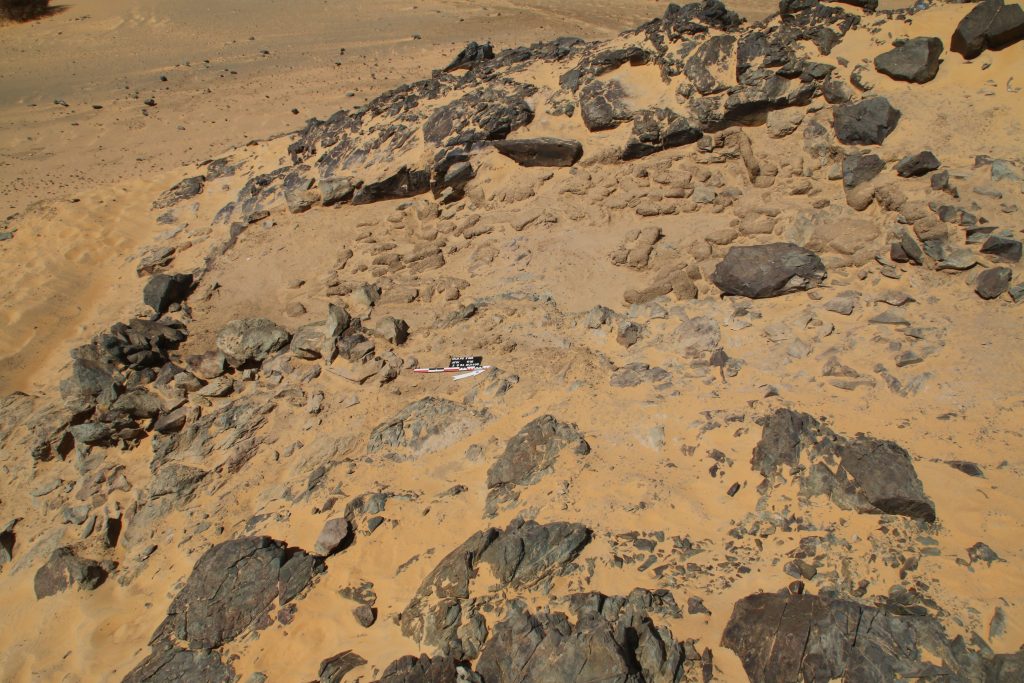
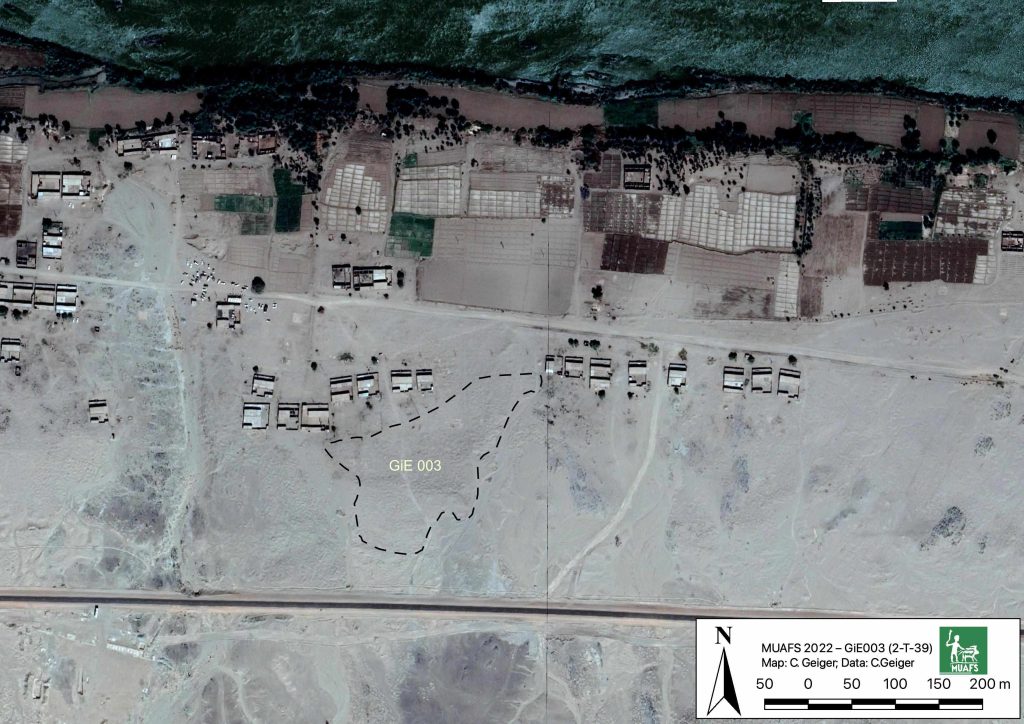
The Kerma cemetery, which Vila documented as 2-T-39, was labelled GiE 003 by the MUAFS project. It comprises an estimated 150 tombs in an area of c. 200 x 100m. The actual extent of the cemetery requires further investigation; in the northern part, the site partially overlaps with the Medieval habitation 2-T-43.
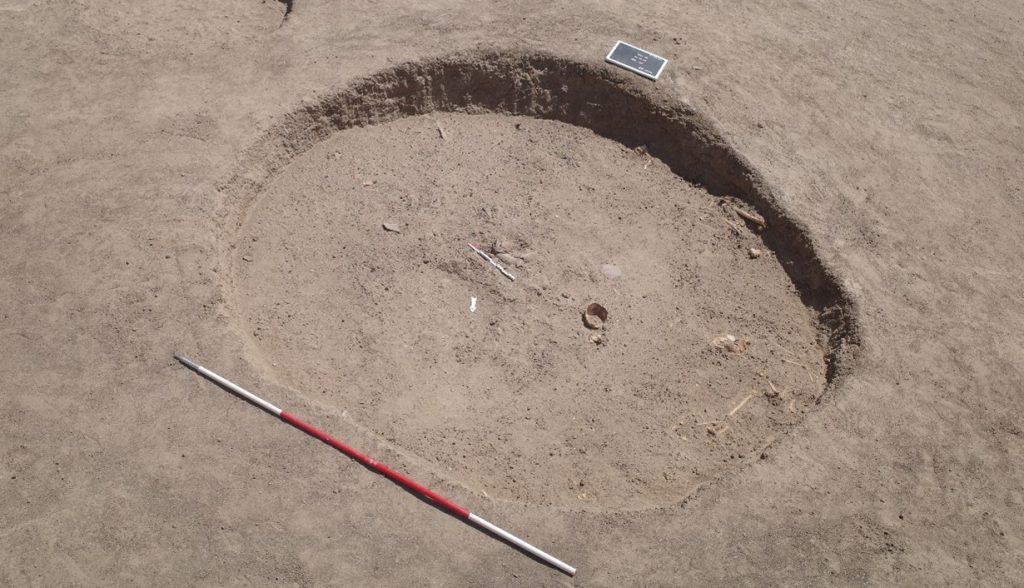
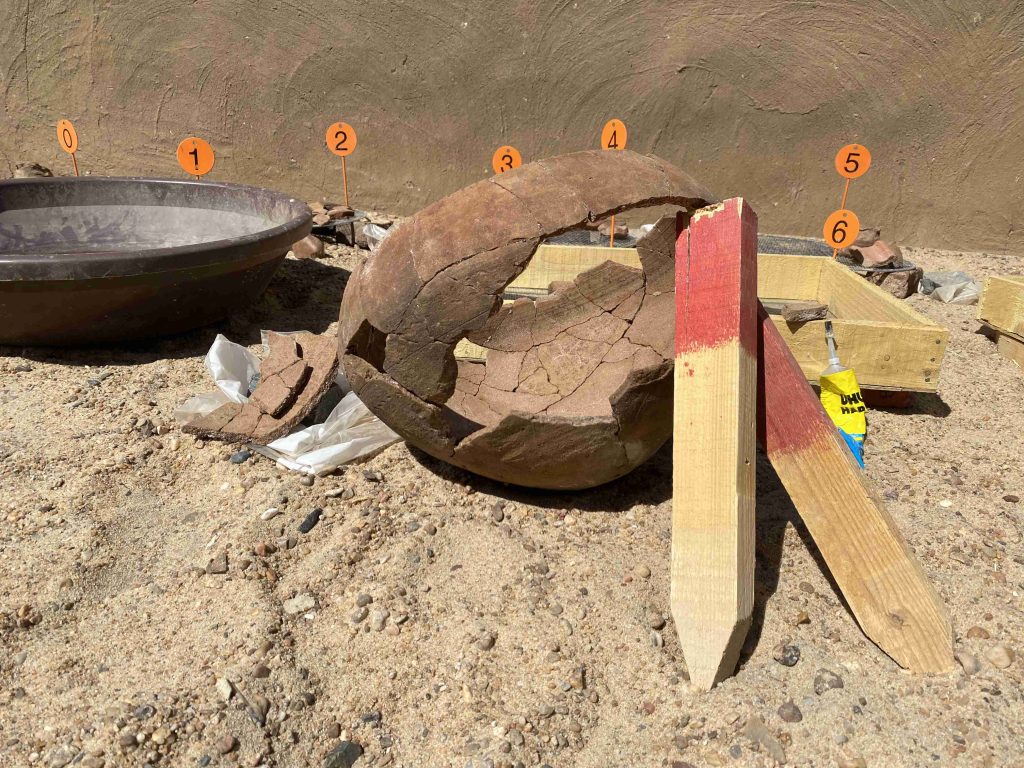
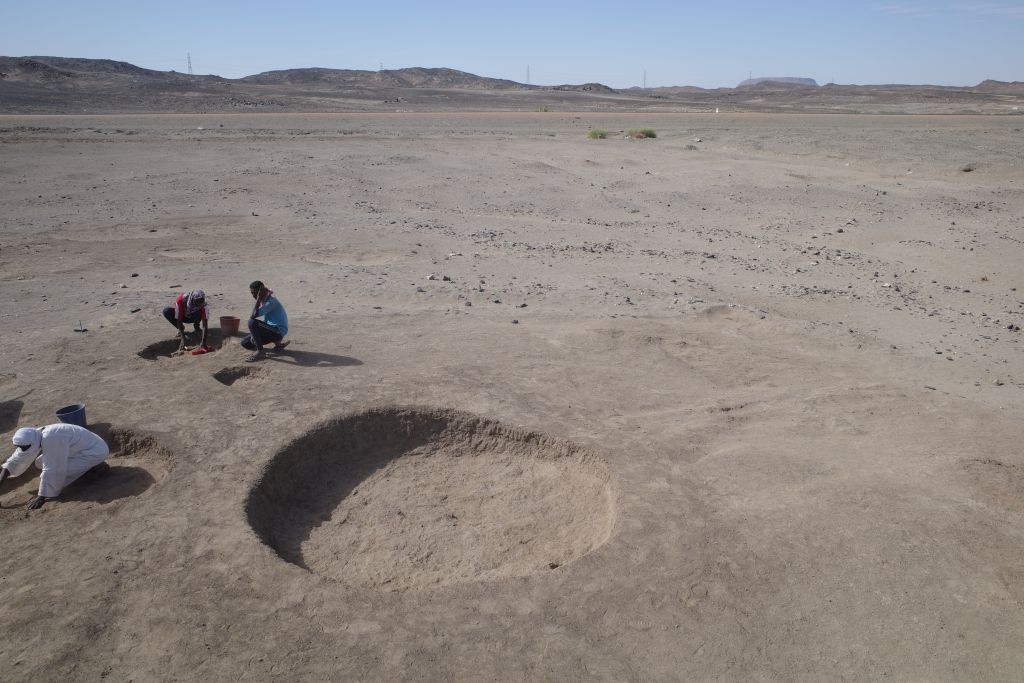
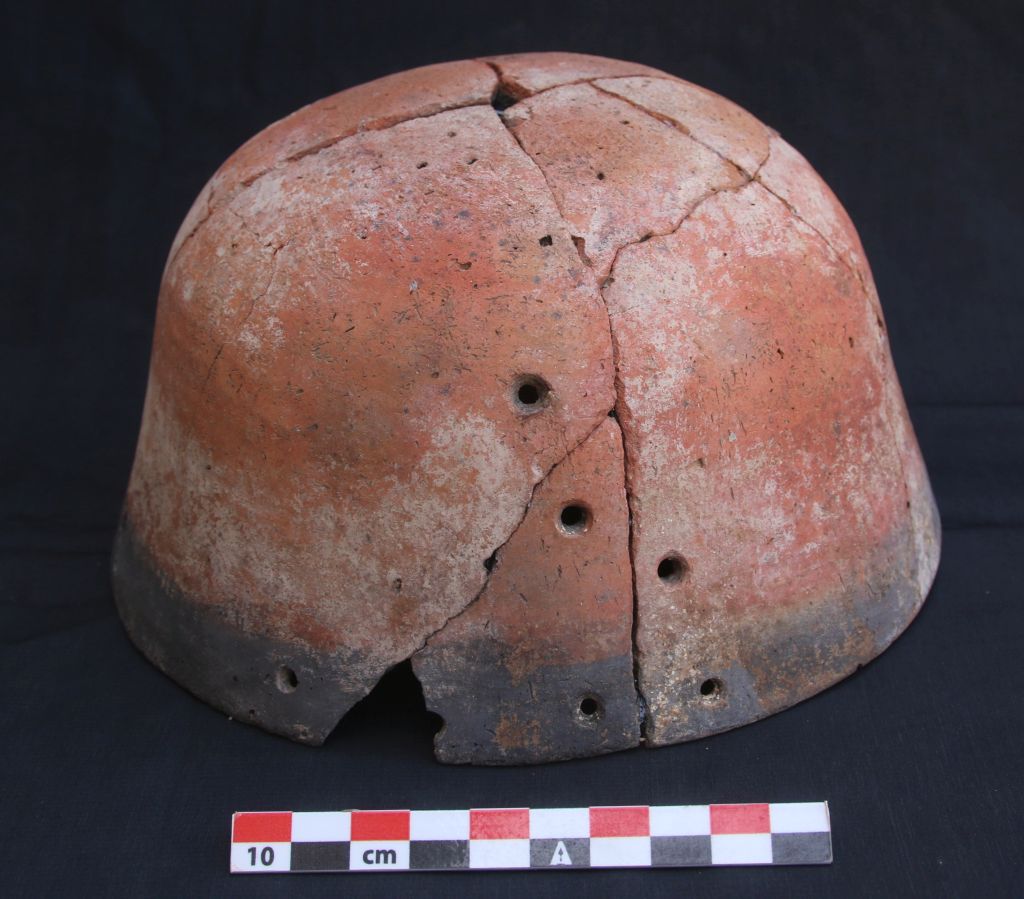
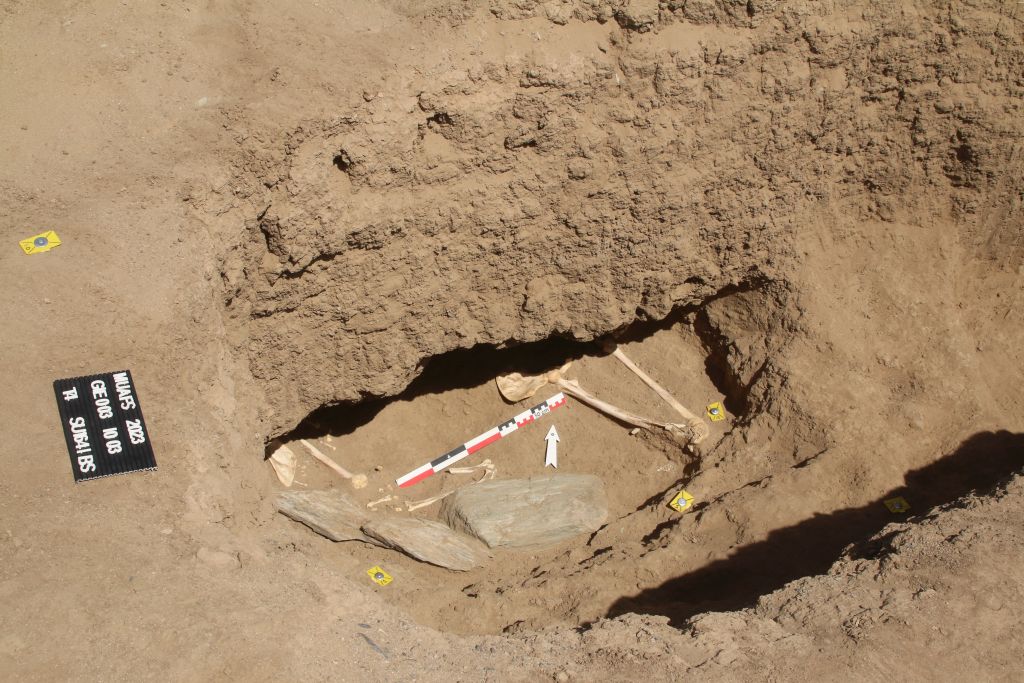
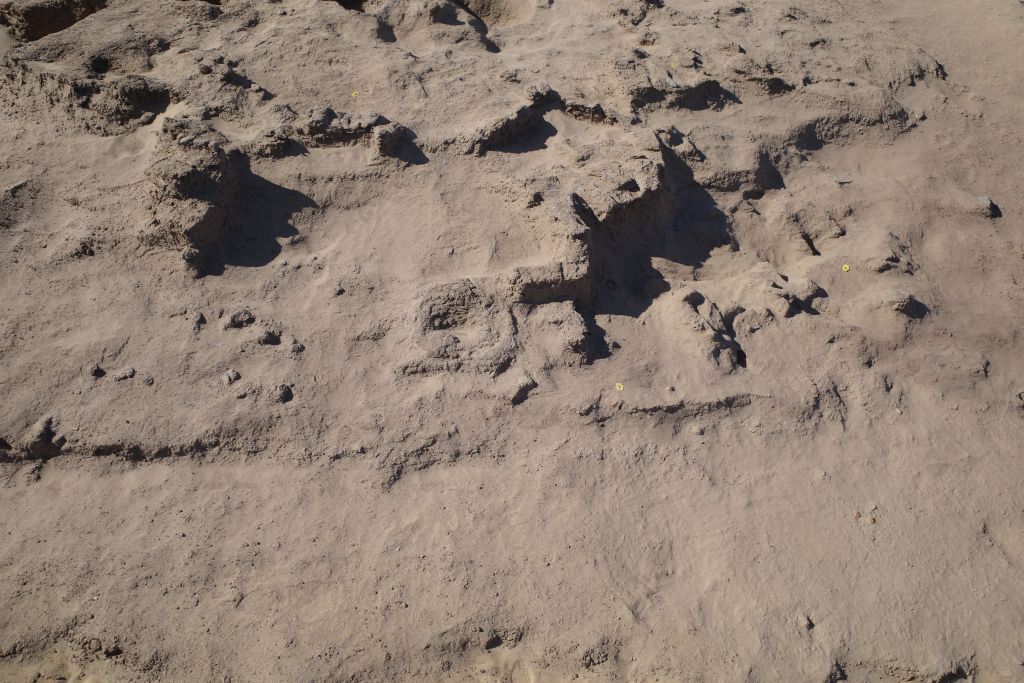
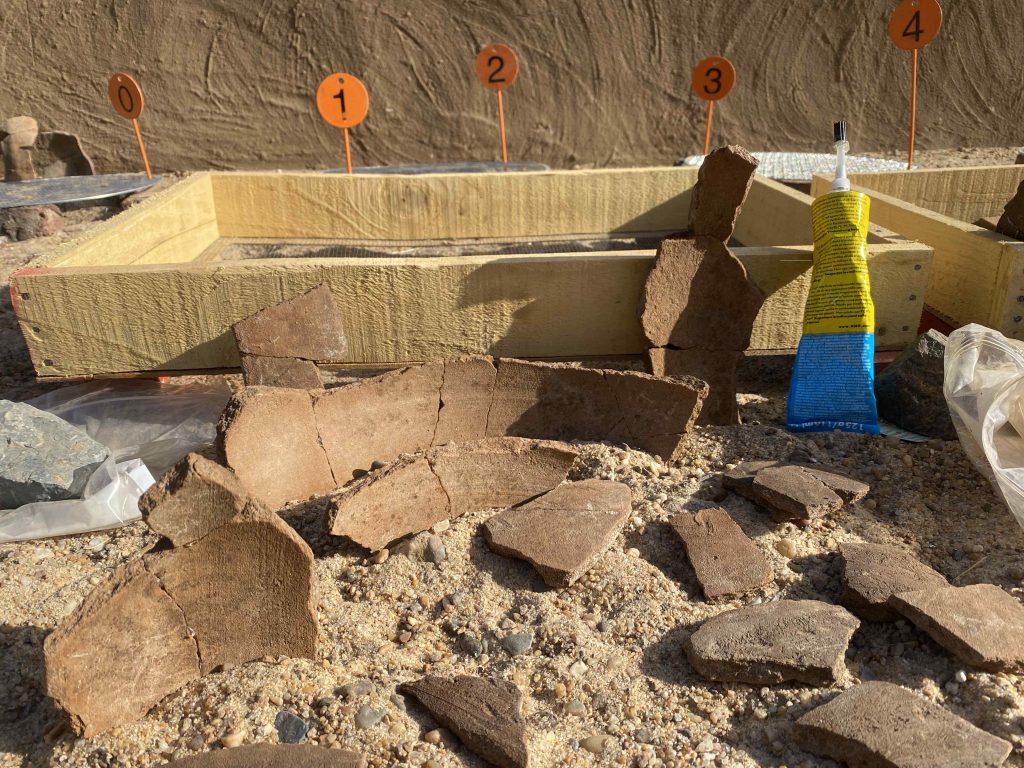
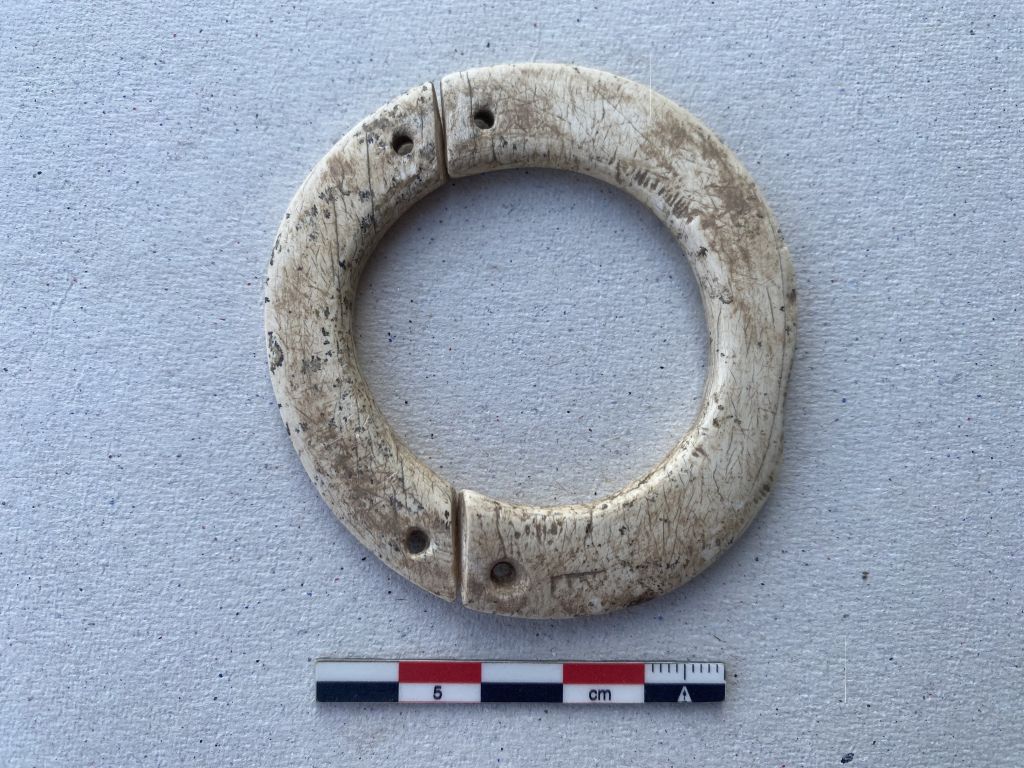
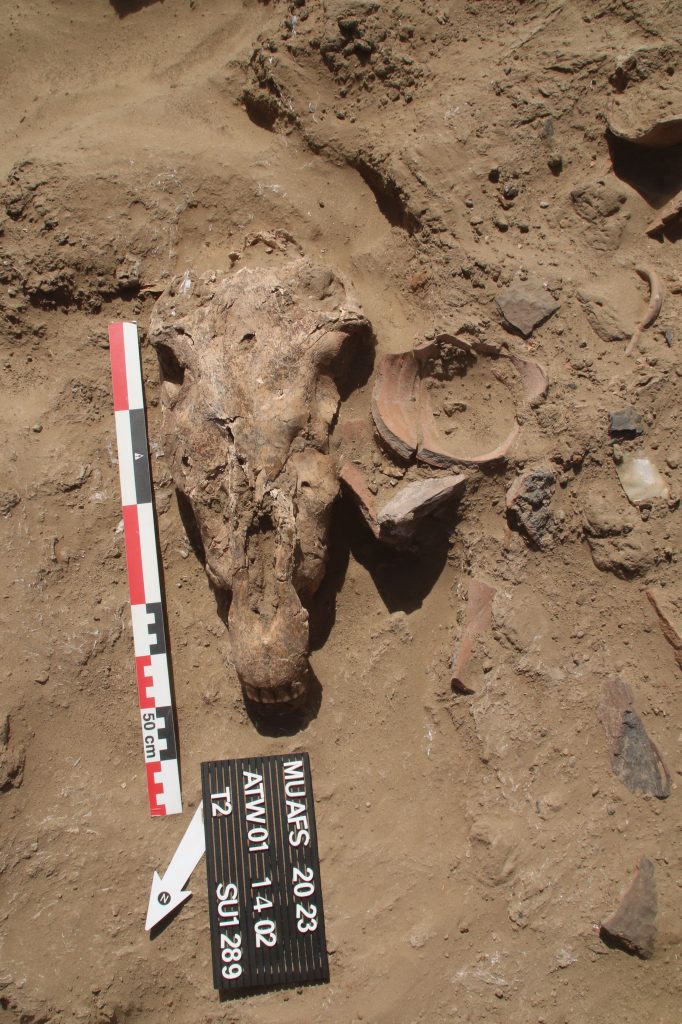
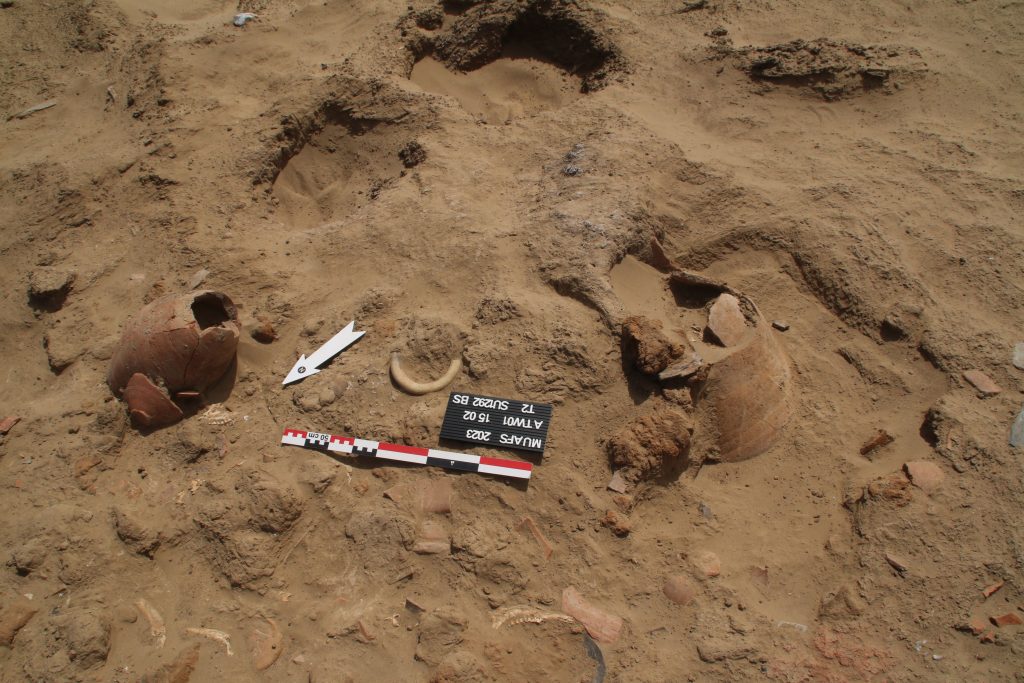
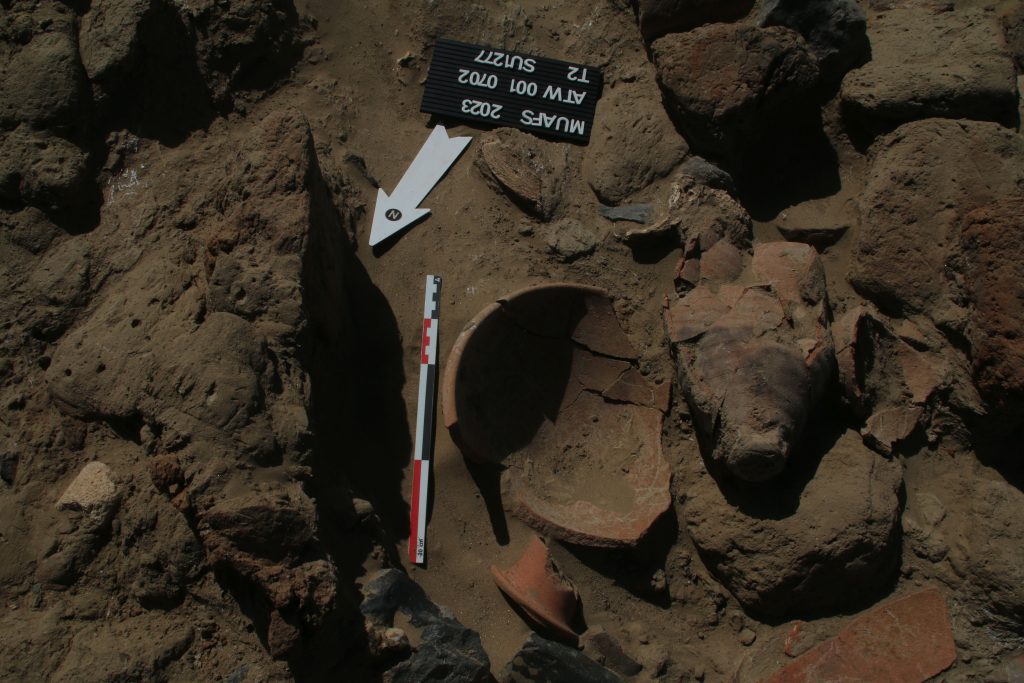
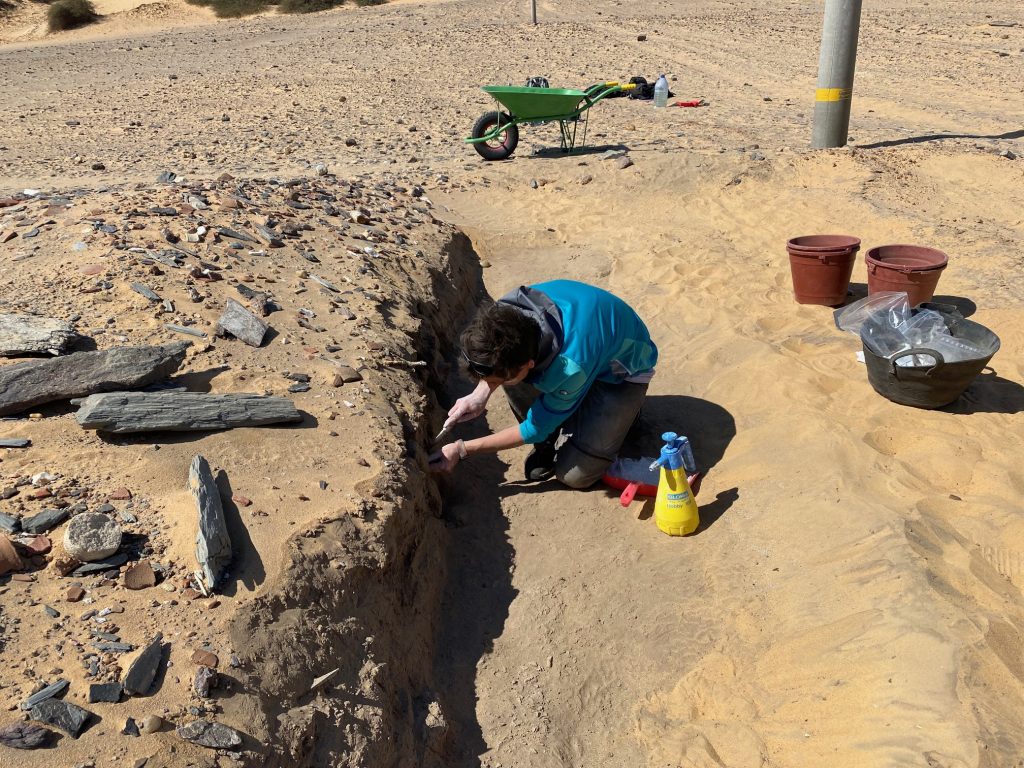
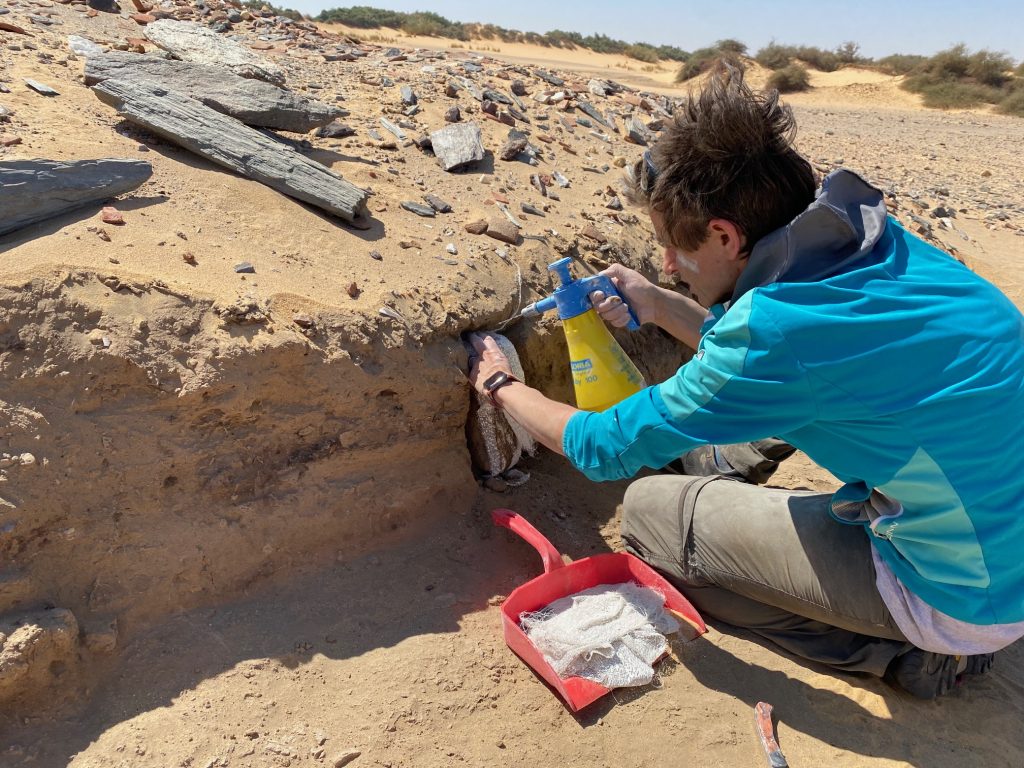
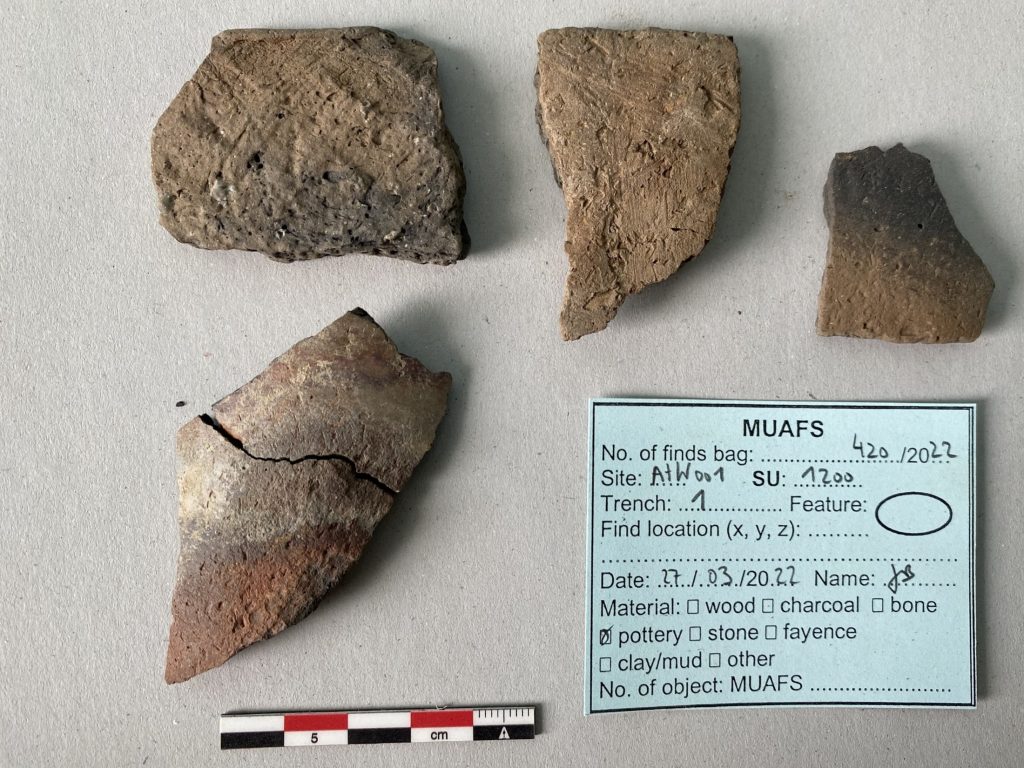
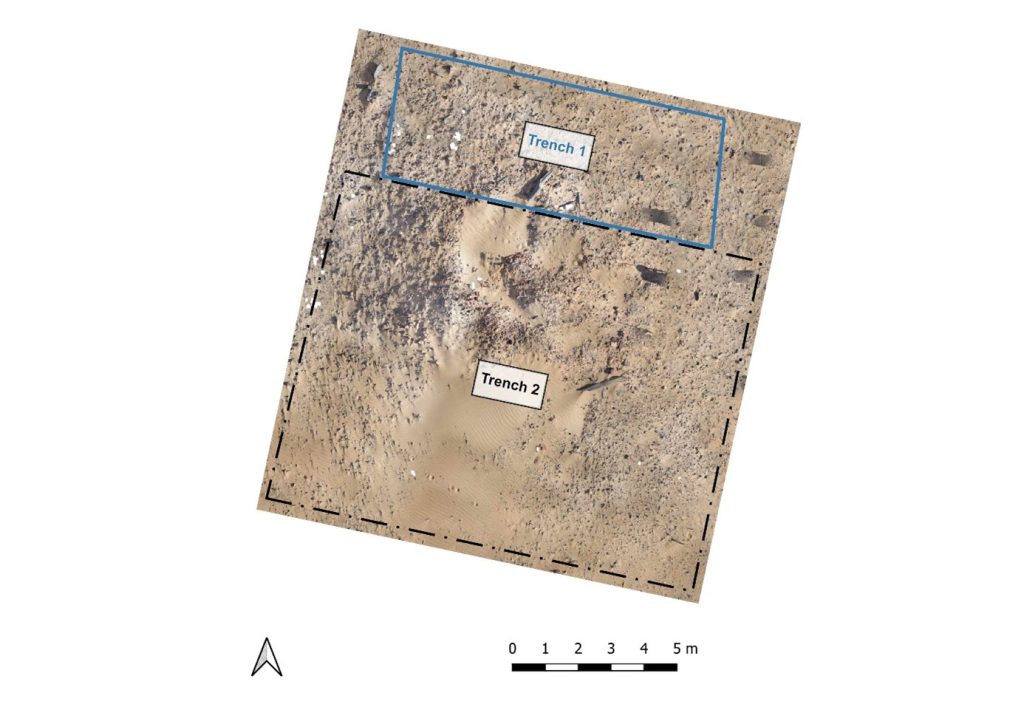
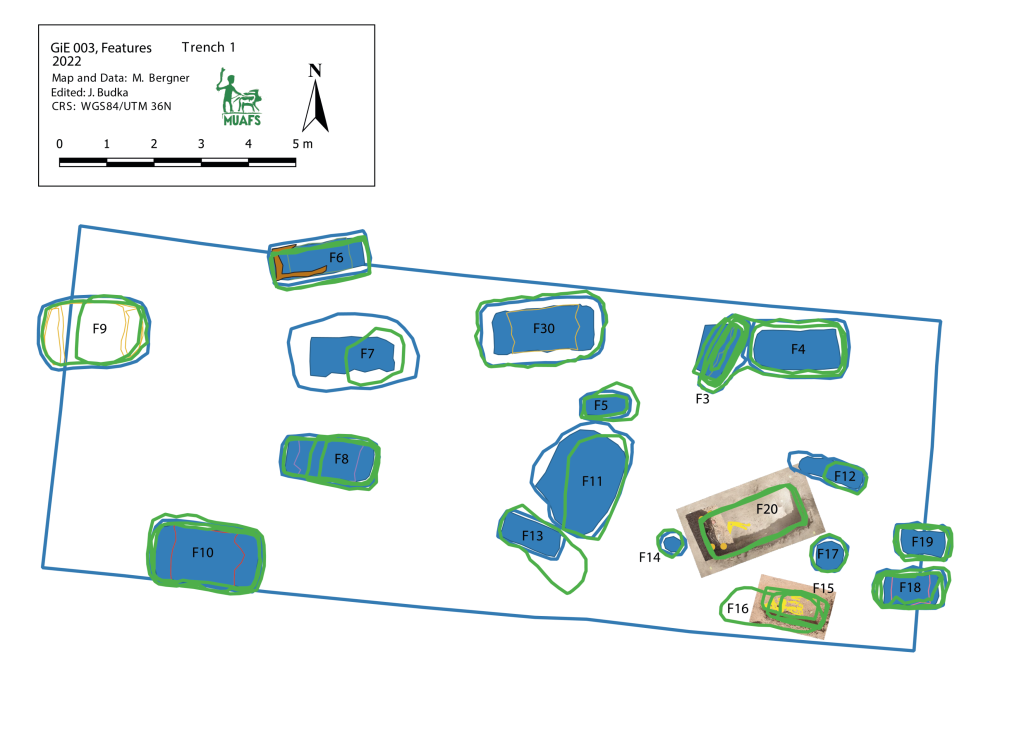
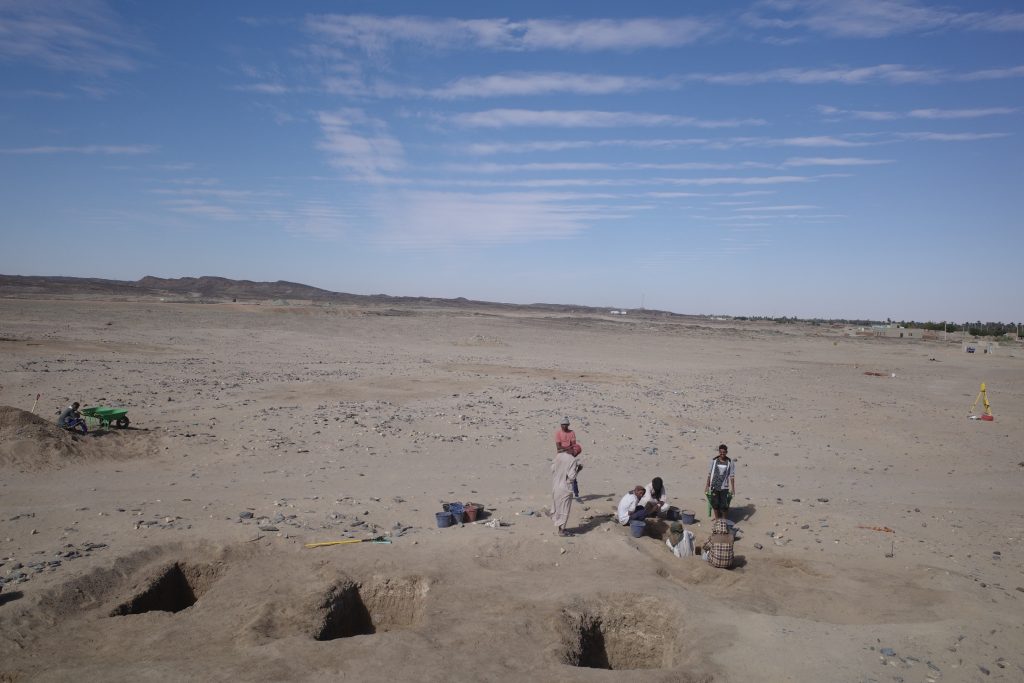
In March 2022, two trenches were opened in GiE 003 and are discussed in the EVO paper. Both trenches had eroded circular tumuli structures on their surfaces, which were covered with pottery sherds and human bones, clearly indicating ancient looting. Despite the age of the looting, some of the Kerma burials unearthed were well preserved and could be dated through the finds. The finds include fly pendants, a scarab with the name of a Hyksos king, a dagger, remains of funerary beds and plenty of beads as well as pottery.
A total of 27 pits were excavated in 2022. Through stratigraphic and pottery analysis it is also possible to make suggestions on the spatial and chronological development of the site. The EVO article is a preliminary assessment based on fieldwork results from 2022, including my detailed study of all the ceramics, but excluding bioarchaeological studies of human and animal bones, as well as the botanical remains.
The most important result of the 2022 excavation is the dating of the southern trench, Trench 2, to the Middle Kerma Period (c. 2000-1750 BCE) and of the northern trench, Trench 1, to the Classic Kerma Period (c. 1750-1500 BCE). This is especially significant, given that there were no notable differences in the surface structures.
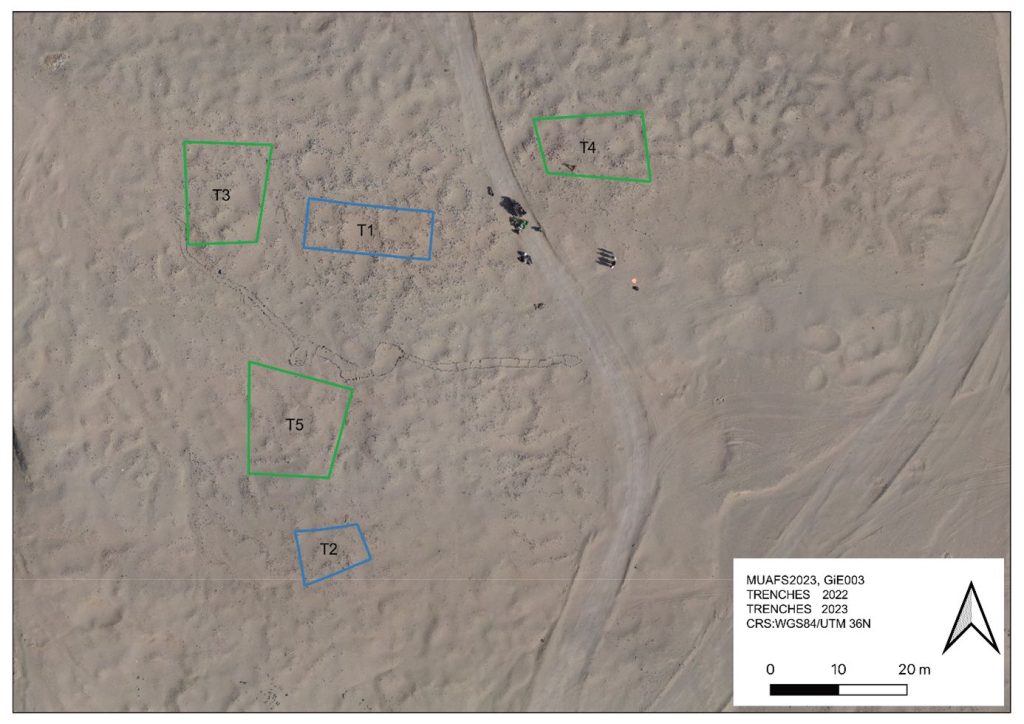
In the EVO article, I proposed a possible relation of the Kerma community using GiE 003 to gold exploitation. First, in the MUAFS concession area, gold-rich quartz-veins have been found in Attab, Ginis, and Kosha, and some archaeological sites point to gold exploitation throughout the centuries, starting well before the Egyptian New Kingdom. Moreover, recent surveys in the Eastern Desert suggest that both control of gold mines and trade relationships with desert nomads played a major role in Kerman access to gold before Egyptian colonisation in the New Kingdom (see Cooper 2021). The affiliation of some of the pottery from GiE 003 with the Pan-Grave horizon seemed to illustrate in 2022 connections to nomadic people, possibly in relation to gold mining. This thesis could now be partly confirmed in 2023: in Trench 5 several Pan-Grave style burials were found (see my short summary of the 2023 season).
Here, I would like to follow Claudia Näser and her appeal for an “archaeology of interaction” (Näser 2012) – during the Kerma period, there were a number of Pan-Grave people present in the Nile Valley and for sure also in the Attab and Ginis area. They were community members (at least seasonally) interacting in various ways with other members – and our focus should be on understanding these interactions and reconstructing them as best we can. This is one of the core interests of the DiverseNile project and will keep us busy in the next years.

Coming back to cemetery GiE 003: one of the results of our excavation work is clearly that funerary practices reflecting social practices in the periphery of the Kerma kingdom must be considered in a more complex light than previously thought. Cultural diversity in the Middle Nile is well traceable during the Middle and Classic Kerma age in terms of architecture, location, burial types and grave goods. However, this requires further material assistance, with a focus on the social impact of cultural contact and the emerging patterns of globalisation during the Kerma kingdom’s heyday. The proximity of Kerma cemeteries (and thus also of possible settlements), especially also of dome grave assemblages well attested in the Attab to Ferka region, to potential gold working sites is clearly an interesting research question to be investigated in the future.
All in all, it seems likely that there was no single Kerman cultural input to interactions with the Hyksos, Egyptians and nomadic people like the Pan-Grave horizon. Rather, we must consider various hierarchical local responses determined by different communities’ ability to consume, shaping what can be called marginal communities in the Kerma state (see also Walsh 2022).
To concluse, the rich finds in GiE 003 enable us to compare this newly excavated Kerma cemetery to the well-known cemeteries of Ukma and Akasha further north. There are very close parallels, as well as notable differences and what appears to be local variations (for details see Budka 2022). This opens new avenues for future research on Kerma communities outside of the Third Cataract region, shifting the focus away from cultural and chronological classification and toward aspects of the social relationships among Middle Nile groups (and their neighbours).
References:
Budka 2022 = J. Budka, Investigating Nubian funerary practices of marginal communities: new evidence from a Kerma cemetery at Ginis, Egitto e Vicino Oriente 45, 2022, 37-62.
Cooper 2021 = J. Cooper, Between the Nile and the Red Sea: Medjay desert polities in the third to first millennium BCE. Old World: Journal of Ancient Africa and Eurasia 1 (1), 2021, 1-22.
Näser 2012 = C. Näser, Nomads at the Nile: towards an archaeology of interaction, in: H. Barnard and K. Duistermaat (eds), The history of the peoples of the Eastern Desert, Los Angeles: University of California 2012, 80-89.
Walsh 2022 = C. Walsh, Marginal Communities and Cooperative Strategies in the Kerma Pastoral State. Journal of Ancient Near Eastern History, 9/2, 2022, 195-220.